Second Trimester
Physical changes
Your uterus is pushing up above the pubic bone and you may have trouble fastening your ordinary clothes.
Now is the time to look for maternity clothing. The second trimester is a perfect time to travel and you may be tempted to plan a holiday.
Sex in pregnancy
This trimester is often the most comfortable time for lovemaking.
- The increase in blood flow may heighten sexual responses. You may feel a sense of increased wellbeing and satisfaction.
- Some women report having erotic fantasies and sexual dreams.
- Expressions of affection and love can continue to be satisfying if you choose not to have intercourse.
Condoms
If you are worried that you or your partner may have HIV or another sexually transmitted disease, it is very important to use condoms during pregnancy to avoid infecting each other.
Baby
The second trimester is the period between four and six months and is known as the growth period, when the already formed organ structures of the foetus enlarge and mature.
Week 13-16: You may feel flutters, which will become more definite kicks and turns. Your baby sleeps and wakes.
Week 24: Your baby measures about 33 cm and weighs about 900 g.
Her skin is covered with a creamy-like protective coating called vernix. Her eyes are open and she can hear sounds. You may be able to tell the difference between an elbow and a foot as your baby kicks against the walls of the uterus.
Mother
The uterus contracts in a weak, painless way, which may only be felt as a hardening of the uterine wall. These contractions are called Braxton Hicks contractions and occur about every 20 minutes throughout pregnancy. They ensure good blood circulation through the uterus and help uterine growth. By the end of the fifth month the top of the uterus, called the fundus, reaches your navel. Your caregiver will determine how far your pregnancy has progressed by measuring the distance, in centimetres, between your pubic bone and the top of your uterus.
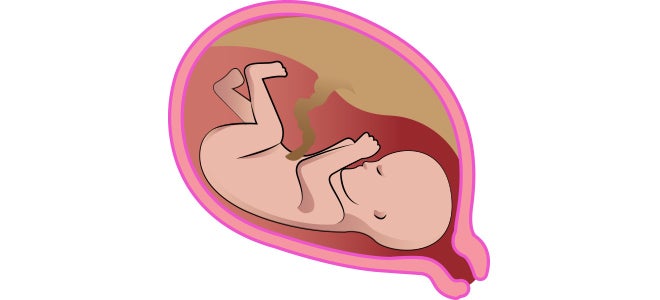
The cervix, or opening of the uterus, is blocked with a plug of mucous. The cervix should remain long, thick and tightly closed during pregnancy.
Your breasts will not increase much in size during the second trimester. Colostrum, a yellowish fluid produced before breast milk, starts to form in the milk glands towards the middle of your pregnancy.
Pigmentation also occurs in areas of your body other than the nipples and areola, due to hormonal changes. If you are dark-haired, lines called linea nigria, will darken between the pubic bone and the navel. Chloasma – “the mask of pregnancy” or facial pigmentation – may appear as brown, irregularly shaped blotches around your eyes and nose. These are due to an overproduction of melanin by the pigment cells, and disappear after the birth of your baby.
Blood volume
| Gestation | Visits, tests, observations | Performed by |
| 16 weeks | Routine observation Amniocentesis – if indicated. |
All caregivers All 15–17 weeks |
| 15–17 weeks |
Routine observation – this will include assessing the frequency of foetal movements. Foetal anomaly scan. |
Obstetrician Midwife |
| 18–24 weeks |
Routine observation – this will include measuring and charting the height of the fundus (the length of the uterus). |
Obstetrician |
| 20 weeks | This very important scan is done at 20 weeks to check the baby’s development. |
Obstetrician |
| 24 weeks | Routine observation. | All caregivers |
The amount of circulating blood increases by up to 40% to meet the demands of the growing uterus and placenta. Physiological anaemia may develop due to the dilution of the red blood cells. This occurs because the liquid part of the blood (plasma) is proportionately greater than that of red blood cells. This can lead to tiredness in late pregnancy.
Physiological anaemia, caused by the dilution of the red blood cells, leads to an iron deficiency, which may cause tiredness and decreased tolerance of exercise.
Tips for expectant moms
- Make appointments for regular prenatal
visits. - Postural correction.
- Pelvic floor exercises.